Unwrapping the Intricacies of Liquid Metal Cooling in Modern Computing
In the fast-paced world of electronics, keeping systems cool is a crucial task. As devices get smaller and more powerful, traditional cooling methods struggle to keep up. Enter liquid metal cooling, an innovative solution that’s turning heads in the tech world. This article dives into its fascinating history, its potential in the current market, and the impact it could have on the future of computing.

A Brush with History: Birth of Liquid Metal Cooling
Liquid metal cooling is not a new concept. It has been used extensively in nuclear reactors since the 1950s, where high heat loads and the need for efficient cooling made it an ideal choice. However, its application in electronics is relatively recent. Early experiments in the 2000s showed promise, but practical problems, like the corrosive nature of liquid metals, kept it out of mainstream use.
Current Developments: Liquid Metal Cooling Breaks into the Mainstream
Fast-forward to today, and the landscape is changing. Tech companies are increasingly turning to liquid metal cooling to keep their high-performance devices from overheating. For instance, Asus has already integrated it into some of their gaming laptops as a means to enhance thermal performance. The result is a cooler, quieter, and more efficient device, which is particularly valuable in the gaming industry, where performance is paramount.
Breaking Down the Tech: How Does It Work?
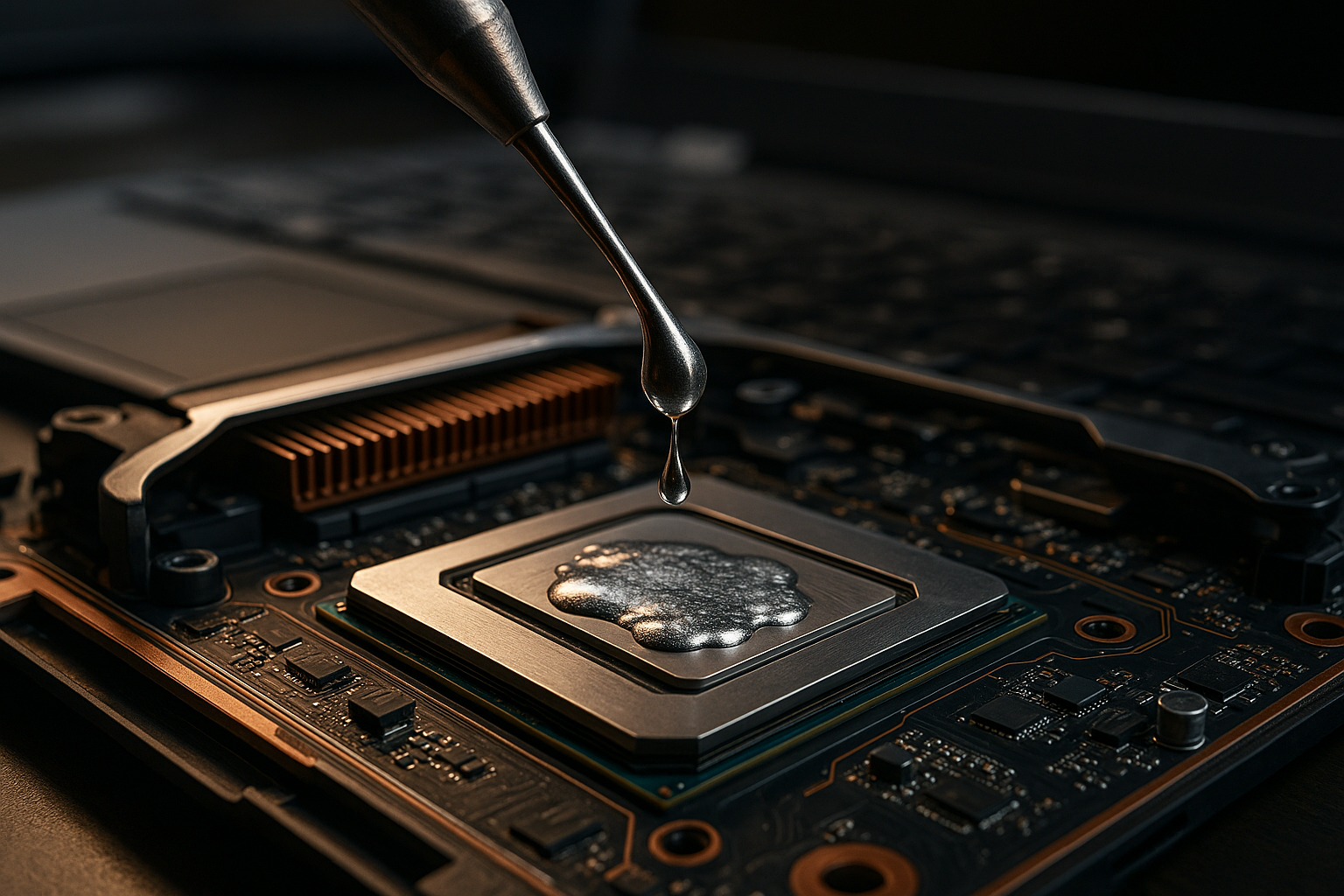
Liquid metal cooling works by replacing the traditional thermal paste between a device’s processor and its heat sink with a layer of liquid metal. The metal has a much higher thermal conductivity than paste, meaning it can transfer heat more efficiently and keep the processor cooler. The challenge lies in finding a metal or alloy that’s both highly conductive and safe to use in electronics. Gallium-based alloys, which are non-toxic and have low melting points, have emerged as a popular choice.
Pricing and Market Impact: From Luxury to Necessity?
At present, liquid metal cooling is still a premium feature, found mainly in high-end gaming laptops and custom-built PCs. However, as the demand for powerful, compact devices grows, it may soon become a necessity rather than a luxury. Market research firm Technavio predicts the global liquid cooling market will grow by over $4.2 billion from 2020 to 2024, an indicator of its potential impact.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Liquid Metal Cooling
The future of liquid metal cooling looks bright. As technology continues to evolve, the need for efficient cooling solutions will only intensify. Researchers are also exploring other applications for liquid metal, such as in wearable devices and even in the human body for medical purposes. While there are still hurdles to overcome, particularly regarding the longevity and safety of the technology, the promise of cooler, more efficient electronics is an exciting prospect.
As the tech world continues its relentless march forward, liquid metal cooling is poised to play a significant role. Its history is fascinating, its potential in the current market is undeniable, and its future is full of exciting possibilities. Whether it’s in the next generation of gaming laptops, wearable tech, or even medical devices, this innovative cooling solution is one to watch.