Rediscovering the Power of Diesel: The Underdog of the Automotive World
Diesel technology has been around for over a century, but it's often overlooked in favor of gasoline engines. This article delves into the history of diesel, its current applications and future prospects, and why it remains a viable alternative in the automotive world.
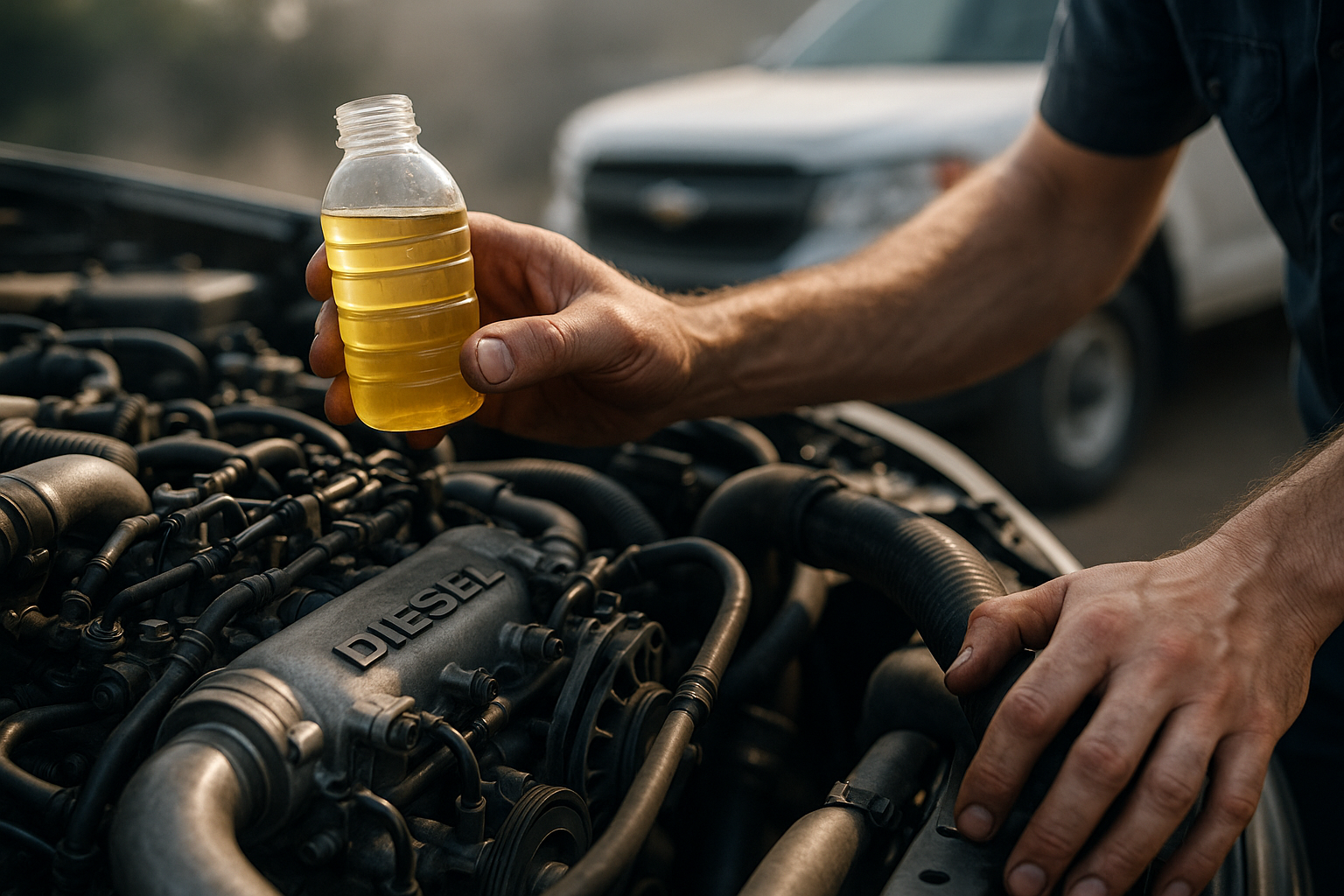

Diesel’s Rich History
Rudolf Diesel invented the diesel engine in the late 19th century. He aimed to create an engine that was more efficient than the steam engines of the time. The first diesel engine ran on peanut oil and was introduced at the 1900 World’s Fair in Paris. Since then, diesel engines have been used in a wide range of applications, from ships and trucks to passenger cars and power plants.
The Mechanics of Diesel Engines
Diesel engines work differently than gasoline engines. They use compression ignition rather than spark ignition, meaning they compress the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder until it heats up and ignites. This process makes diesel engines more energy efficient than their gasoline counterparts. Additionally, diesel fuel has a higher energy density than gasoline, which contributes to the superior fuel economy of diesel vehicles.
The Rise of Diesel in the Automotive Industry
Despite their efficiency, diesel engines were largely relegated to heavy-duty applications for much of the 20th century. However, the oil crises of the 1970s spurred interest in more fuel-efficient vehicles, leading to a boom in diesel passenger cars. Diesel cars became particularly popular in Europe, where high fuel prices made their superior fuel economy an attractive proposition.
Diesel in the Modern Era
In the 21st century, diesel engines have faced challenges due to concerns about air pollution and climate change. Diesel engines emit more particulate matter and nitrogen oxides than gasoline engines, which has led to stricter emissions standards. However, advances in diesel technology, such as particulate filters and selective catalytic reduction systems, have significantly reduced these emissions.
Diesel’s Future Prospects
Despite the challenges, diesel remains a viable alternative in the automotive world. Diesel engines are still more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines, and they also produce less carbon dioxide per mile driven. Furthermore, diesel vehicles are renowned for their durability and longevity, which can make them a cost-effective choice in the long run. With the advent of cleaner diesel technologies and biofuels, diesel has the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable transportation future.
In conclusion, while diesel may be an underdog in the automotive world, it has a rich history and a promising future. Its superior fuel efficiency, durability, and potential for sustainability make it a compelling option for drivers and industry alike. As we navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21th century, the humble diesel engine may yet have its day in the sun.